In reality, most EV charging is done at home and that’s part of the appeal. No more tedious stopping at filling stations when you just want to be somewhere else, no more paddling around in puddles of spilt diesel or queuing to pay. Just go home and plug in. It’s that simple. The car will fill itself up while you sleep, eat or watch the telly. It's incredibly convenient, but you will need to think about how it is going to work - so this is our guide to charging an electric vehicle at home.
What do I need to charge an electric car at home?
There are two main types of charger you can use at home, the slowest is a 2.4kW trickle charger, also known as a granny charger, which plugs straight into a 13 amp socket just like any other household appliance. No electrical installation work is needed to use one.
The second is a charge point installed on the wall of your property. Charge points are the faster option and available at three levels of power, 3.6kW (classified as slow) 7kW (fast) or 22kW (fast). The 22kW option requires an expensive, industrial 3-phase electrical feed.
Which is the best choice of home charger?
Trickle chargers are sometimes supplied with an electric vehicle as standard or as an option from new or you can buy one from third party suppliers. They plug straight in to a household 13amp socket, draw a maximum of 10 amps and charge at 2.4kW.
Most modern EVs can fast charge from a domestic AC supply at around 7kW and so a 7.2kW wall box is the most common choice. 3.6kW wall chargers are designed for older cars like the early Nissan Leaf which as standard could only charge from AC at 3.3kW. An early Leaf can be plugged into a 7kW wall charger but will still only charge at 3.3kW, so it makes sense to fit the more powerful charger in case you decide to switch to a more modern EV later.
A 7kW charger will charge at twice the speed of a 3.6kW charger if you have an electric vehicle that can accept it. You can see reviews and learn more about these on our charging pages.
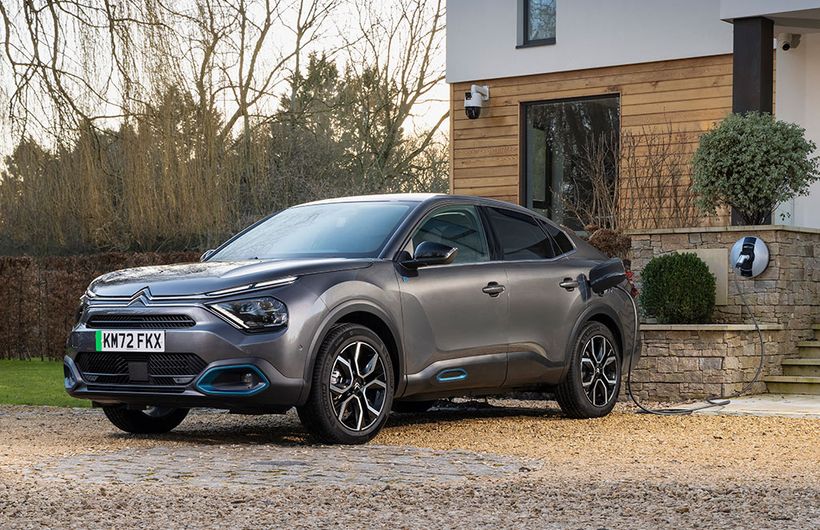 A 7.2kW wall box is the most common type of home charger
A 7.2kW wall box is the most common type of home charger