The car industry is undergoing one of the biggest changes in its history. Electrification is introducing an exciting new world of possibilities where personal mobility has the potential to be cleaner and more efficient than ever. But driving an electric car powered by green electricity is only one part of the drive to reduce carbon emissions. To really help make a difference, you need to look beyond the cars themselves to the processes and materials that go into their production.
Hyundai knows that reducing emissions and improving sustainability during the design and production process is an essential part of building a cleaner, more responsible future. As part of the brand’s ‘Progress for Humanity’ movement, Hyundai is clearly dedicated to powering the future of mobility.
To achieve that goal, the brand is thinking big. Really big. The Hyundai Motor Company has a worldwide target of selling two million battery electric cars a year by 2030 and is set to introduce 11 new all-electric models between now and then.
Driving Hyundai’s commitment is its IONIQ brand which ushers in a new era in connected, sustainable mobility. Launched in 2015, the range currently consists of two ground-breaking models, the IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 6, both based on the industry leading Electric Global Modular Platform (E-GMP).
With innovative interiors and advanced technologies, including 800-volt charging capability and Vehicle-to-Load functionality, both models redefine what drivers, passengers and owners can expect from an electric car.
While the advanced technical features of the Hyundai IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 6 offer obvious, immediate advantages such as ultra-fast charging and high efficiency, both models showcase the brand’s ongoing commitment to sustainable production and materials.
Surfaces with stories to tell
IONIQ 5
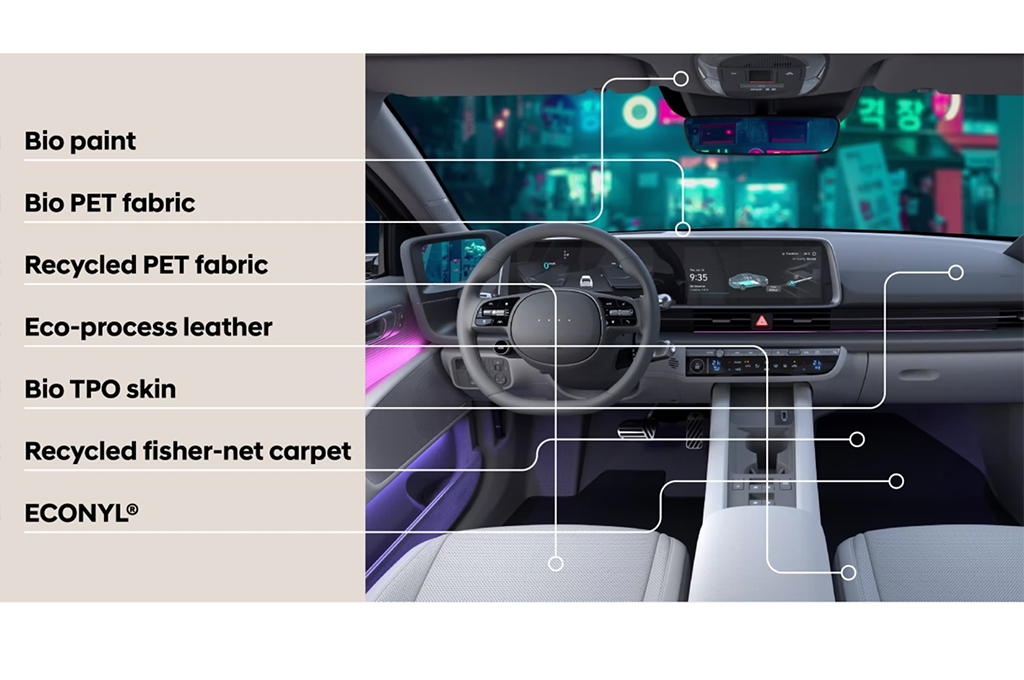
Sustainability is at the centre of IONIQ’s vision, and evidence of Hyundai’s forward-thinking approach is evident in numerous places both inside and outside the car. The IONIQ 5, for example, features seat coverings and door armrests constructed using yarn that comprises up to 39 per cent recycled material. As a result, the IONIQ 5’s interior contains the equivalent of 32 recycled plastic bottles. Hyundai estimates that this reduces the carbon dioxide emissions in the production of these parts by an impressive 70 per cent.
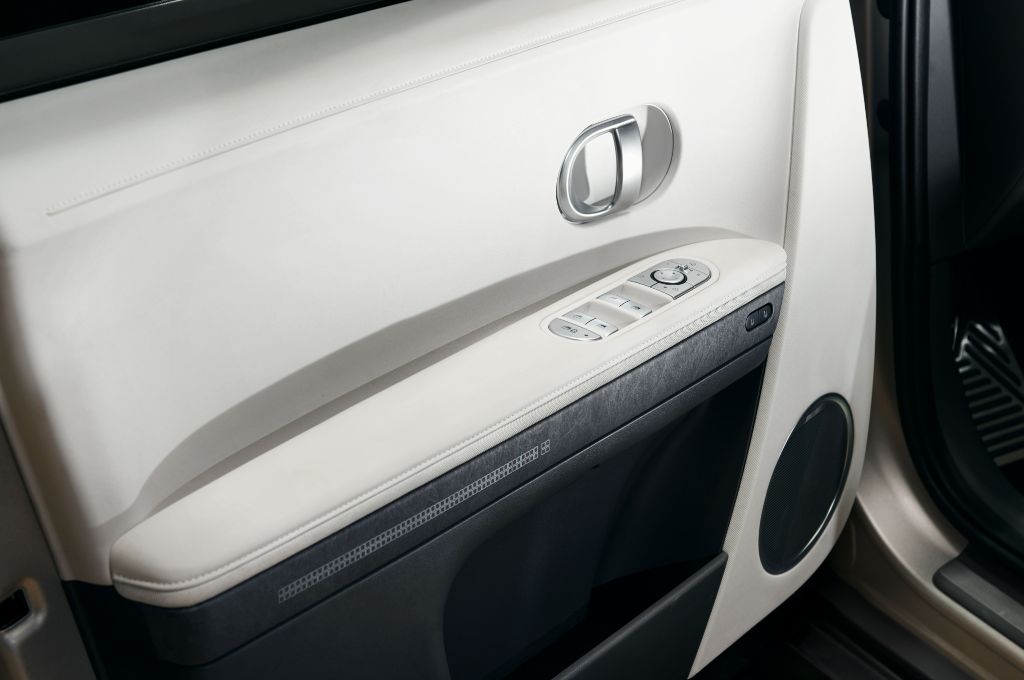

On models with leather trim, the seat and door armrest coverings feature eco-processed leather that is dyed and treated with flaxseed extracts. By using these instead of from animal-derived oils, water consumption is significantly reduced in the leather dyeing process.
Such is Hyundai’s commitment to sourcing sustainable and recyclable materials that almost every surface has a story to tell. Bio PET fabric, another sustainable yarn (made from recycled plastic packaging), is used in the headliner, seat coverings, and floor of both IONIQ models. This innovative textile is made from organic ingredients including sugar cane and corn which significantly reduces the need for oil-based ingredients. This, in turn, reduces the carbon dioxide emissions from production of these parts by 63 per cent.
Other sustainable materials used in the IONIQ 5 are Bio-TPO+ and PP yarn. These contain extracts from natural sugarcane and are up to 22 percent organic material.
The striking paperette material used in the detailing of IONIQ 5’s doors is made from High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) – a100 per cent recyclable and reusable material that free from harmful substances, while the door trim, door switches and modular crash pads are painted with bio paints, containing up to 13 per cent bio polyol. The bio paints contain biomaterial from corn, palm, and bean oil as well as grape tannin extract.
Finally, the floor mats are made from 100% ECONYL®, a regenerated nylon yarn made of nylon waste, including fishing nets recovered by Healthy Seas, the marine conservation organisation that has worked in partnership with Hyundai since 2021.
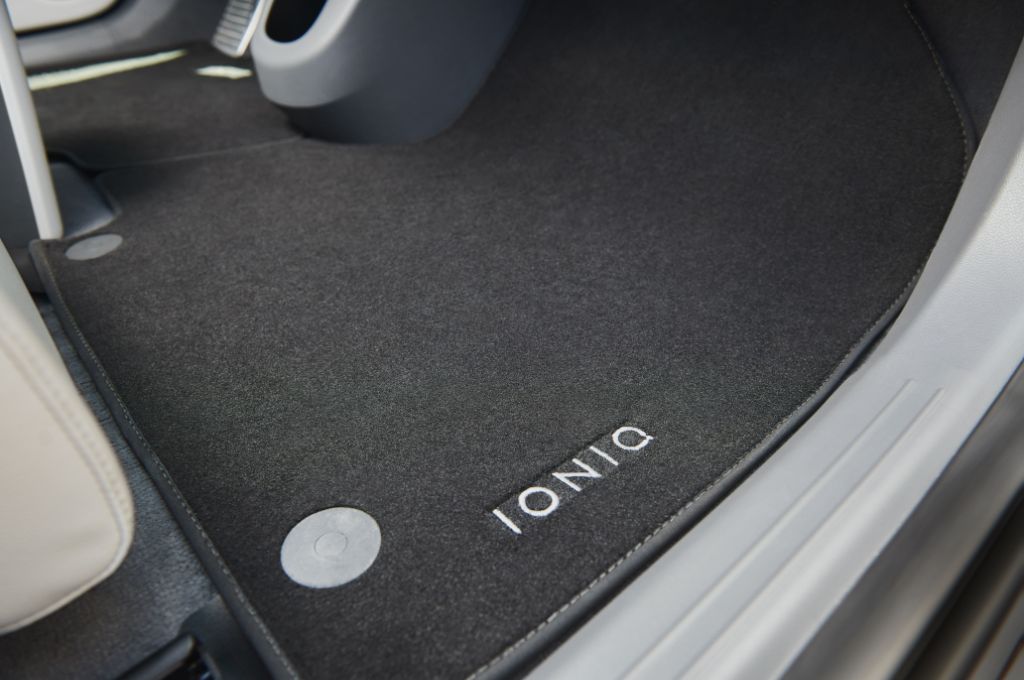

IONIQ 6
Launched in 2022, the IONIQ 6 features a host of innovative materials that significantly reduce the environmental impact of the vehicle’s production. Like the IONIQ 5, it uses bio PET fabric (made from recycled plastics) in the headliner, bio paint derived from vegetable oils in the doors, and recycled PET fabric and eco-process leather in the seats.
The IONIQ 6 also features a dashboard constructed with a bio TPO skin – another hardwearing material which contains 12 per cent bio PET(recycled clear plastics) – while the floor carpets contain up to 20 per cent nylon from recycled fishing nets.
Like the IONIQ 5, the IONIQ 6’s floor mats are also fully made from ECONYL®, while exterior trim panels are coloured using recycled pigment paint from end-of-life tyres.
Taking drag to a new low and range to a new high
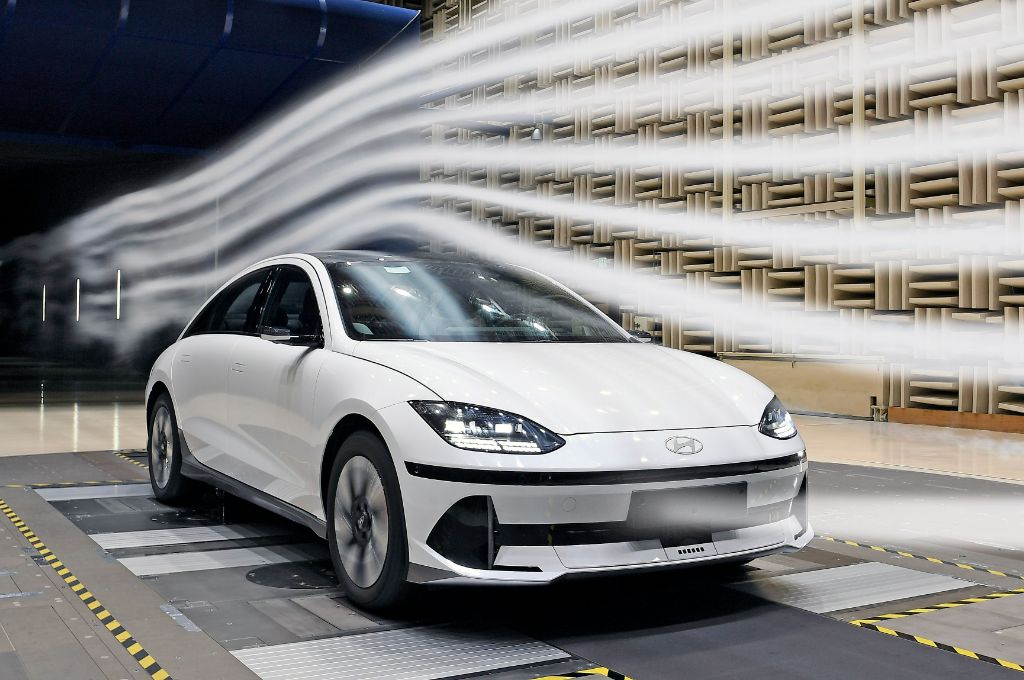
In addition to the extensive use of sustainable and recycled materials, the IONIQ 6 takes efficiency to a new level thanks to its innovative ‘streamliner’ design. Inspired by iconic streamliner cars of the 1940s and 50s, along with classic aeroplanes such as the Supermarine Spitfire, the IONIQ 6 has a drag coefficient of just 0.21, which helps deliver a WLTP driving range of up to 338 miles* (IONIQ 6 Premium 77 kWh 228PS RWD).
To help achieve this remarkable figure, Hyundai’s design and engineering teams developed a host of innovative features that define the look of the car. They include two active air flaps at the front (which also feature on the IONIQ 5), wheel air curtains and an integrated rear spoiler that features a Spitfire-inspired winglet that absorbs the air flow from the roof and reduces drag by minimising vortices at the spoiler’s tip.
Another innovation developed for the IONIQ 6 is a wheel gap reducer that minimises the empty space between the front bumper and the tyres. The reducer overcomes the aerodynamic challengers created by the IONIQ 6’s short front overhangs and improves airflow around the wheel wells. Further aerodynamic aids include a full underfloor cover, optimised deflectors and separation traps on both sides of the rear bumper.
The IONIQ 5 and IONIQ 6 showcase some of the most advanced design and engineering features in the industry and show that building cars sustainably has benefits to both the environment and owners.

*IONIQ 6 Premium 77 kWh 228PS RWD MY23 maximum electric range 338 miles. CO2 emissions: 0 g/km. These figures were obtained after the battery had been fully charged. The electric range shown was achieved using the WLTP test procedure. Figures shown are for compatibility purposes. Only compare fuel consumption, CO2 and electric range figures with other cars tested to the same technical procedures. These figures may not reflect real life driving results, which will depend upon a number of factors including road conditions, outdoor temperature, driving style, use of climate control and battery condition.
IONIQ 5 Premium 77 kWh 228PS RWD MY23 maximum electric range 315 miles. CO2 emissions: 0 g/km. These figures were obtained after the battery had been fully charged. The electric range shown was achieved using the WLTP test procedure. Figures shown are for compatibility purposes. Only compare fuel consumption, CO2 and electric range figures with other cars tested to the same technical procedures. These figures may not reflect real life driving results, which will depend upon a number of factors including road conditions, outdoor temperature, driving style, use of climate control and battery condition.